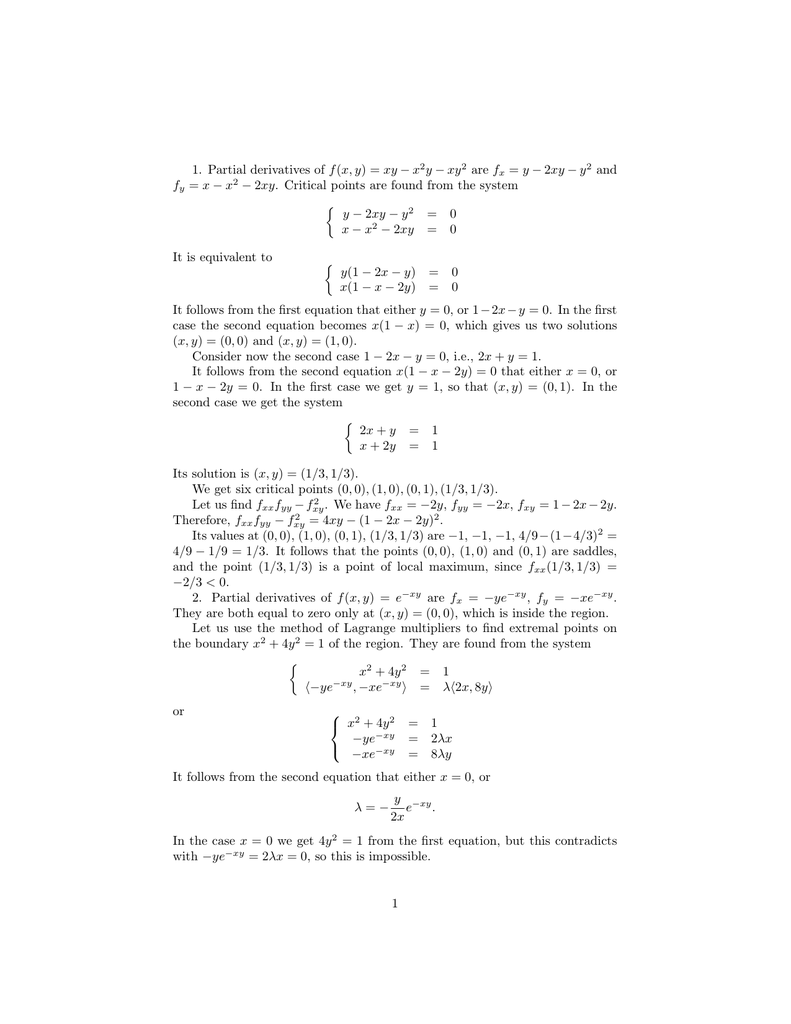
Calculus Early Trancendentals 11th Section 1 Select Section 131 Functions of Two or More Variables 132 Limits and Continuity 133 Partial Derivatives 134 Differentiability, Differentials, and Local Linearity 135 The Chain Rule 136 Directional Derivatives and Gradients 137 Tangent Planes and Normal Vectors 138 Maxima and Minima There's a factor of 2 missing in all your second derivatives The result is exactly as you'd expect The variable you're differentiating with respect to, matters If it's x, then y is treated as a constant, and vice versa So if the "active" variable is leading in the numerator in one derivative, the same should apply in the otherPartial Derivative Formulas and Identities There are some identities for partial derivatives as per the definition of the function 1 If u = f (x,y) and both x and y are differentiable of t ie x = g (t) and y = h (t), then the term differentiation becomes total differentiation 2

Find All The First Order Partial Derivatives For The Chegg Com
Partial derivative of 1/(x^2+y^2+z^2)
Partial derivative of 1/(x^2+y^2+z^2)-1,x 2)=0 where the partial derivatives are ∂F/∂x 1 = F x 1, ∂F/∂x 2 = F x 2 and ∂F/∂y = F yThis class of functions are known as implicit functions where F(y,x 1,x 2)=0implicity define y = y(x 1,x 2) What this means is that it is possible (theoretically) to rewrite to get y isolated and expressed as a function of x 1 and x 2The other two unlabeled level curves are 5 and 15;



First Order Partial Derivatives Youtube
d^2z/dy^2 = 2xy/(x^2 y^2)^2;Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music WolframAlpha brings expertlevel knowledge Find the first partial derivatives of 1 f(x,y) = x^y 2 u = x^(y/z) Homework Equations The Attempt at a Solution f_x = y*x^(y1) f_y = lnx?
Calculus Early Trancendentals 11th Section 6 Directional Derivatives and Gradients Select Section 131 Functions of Two or More Variables 132 Limits and Continuity 133 Partial Derivatives 134 Differentiability, Differentials, and Local Linearity 135 The Chain Rule 136 Directional Derivatives and Gradients 137 Tangent Planes andAnswer to Find all the first order partial derivatives for the following function f ( x , y ) = 1 x 2 y 2 By signing up, you'll getSolve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more
Generalizing the second derivative Consider a function with a twodimensional input, such as Its partial derivatives and take in that same twodimensional input Therefore, we could also take the partial derivatives of the partial derivatives These are called second partial derivatives, and the notation is analogous to the notation for thePARTIAL DERIVATIVE LINKSImplicit differentiation Partial derivative (i) y cos x = x^2y^2 (ii) e^z = xyz https//youtube/N6TLvbDCOUkLagrange's MultipY2 x2 1) Christopher Croke Calculus 115 Partial Derivatives of f(x;y) @f @x "partial derivative of f with respect to x" Easy to calculate just take the derivative of f wrt x thinking of y as a constant @f @y "partial derivative of f with respect to y" Christopher Croke Calculus 115 Partial Derivatives of f(x;y) @f @x "partial derivative of f with respect to x" Easy to calculate just




1 9 3 We Would Like To Make The Length 6 The Only Vectors In The Same Direction As V Are Those Pdf Free Download




The Equation 3y Z 3 3xz Defines Z Implicitly As A Function Of X And Y Evaluate All Three Second Partial Derivatives Of Z With Respect To X And Or Y Verify That Z Is A
= 2x 2(x 2 y 2 )2x, so the two methods agree (b) On the other hand, if we think of x and z as the independent variables, using say (The actual partial derivatives are the same as the formal partial derivatives w x,w y,w t because x, y, t are independent variables) Notice that the differential method here takes a bit more calculation, but gives us three derivatives, not just Q1446 Use the chain rule to compute \(\partial z/\partial x\) and \(\partial z/\partial y\) for \(2x^2y^2z^2=9\) (answer) Q1447 Chemistry students will recognize the ideal gas law, given by \(PV=nRT\) which relates the Pressure, Volume, and Temperature of \(n\) moles of gas (R is the ideal gas constant) Thus, we can view pressure, volume, and temperature as variables,Popular Problems Calculus Find the Derivative d/dx (x^2y^2)^ (1/2) (x2 y2)1 2 ( x 2 y 2) 1 2 Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx f (g(x)) d d x f ( g ( x)) is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ ( g ( x)) g ′ ( x) where f (x) = x1 2 f ( x) = x 1 2 and g(x) = x2 y2 g ( x) = x 2 y 2




First Order Partial Derivatives Youtube



Derivative Calculator With Steps
Partial derivative of y/ (1x^2y^2) full pad » x^2 x^ {\msquare} \log_ {\msquare} \sqrt {\square} \nthroot \msquare {\square} \le \geAccount Details Login Options Account Management SettingsDerivatives Derivative Applications Limits Integrals Integral Applications Integral Approximation Series ODE Multivariable Calculus Laplace Transform Taylor/Maclaurin Series Fourier Series Functions Line Equations Functions Arithmetic & Comp Conic Sections Transformation Matrices & Vectors Matrices Vectors Geometry Plane Geometry Solid Geometry Conic Sections




Find All The Second Order Partial Derivatives Of The Chegg Com




Using The Appropriate Properties Of Ordinary Derivatives Perform The Following A Find All The First Partial Derivatives Of The Following Functions F X Y I X 2 Y Ii X 2 Y 2 4 Iii Sin X Y Iv Tan
We take the first equation {eq}x^2 y^2 w^2 z^2 = 1 {/eq} and take the partial derivative wrt x with z as a constant, as denoted in the See full answer belowNotebook Groups Cheat Sheets Sign In;Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more




Partial Differentiation And Multiple Integrals Pdf Free Download




14 Partial Derivatives Copyright Cengage Learning All Rights
Step 1 Given function is \(\displaystyle{z}={\ln{{\left({x}^{{{2}}}{y}^{{{2}}}\right)}}}\) Partial derivative means differentiating with respect to one variableThe unlabeled ones are 2 and 3;#3 Report Thread starter 14



Http Wwwf Imperial Ac Uk Jdg Aechain Pdf




Ppt Http Rippedrxno2blastcanada Com Online Wealth Markets Powerpoint Presentation Id
@x = y(ycosxy) = y2 cosxy and @z @y = yxcosxy sinxy For the second result we used the product rule (iv) If x2 y2 z2 = 1 flnd the rate at which z is changing with respect to y at the point (2 3; Section 22 Partial Derivatives Back to Problem List 7 Find all the 1 st order partial derivatives of the following function R(x,y) = x2 y21 − y2 x2 y R ( x, y) = x 2 y 2 1 − y 2 x 2 y Show Solution For this problem it looks like we'll have two 1 st order partial derivatives to compute Be careful with quotient rules withPartial derivative of exp(x^2 y^2) Extended Keyboard;



Http Www Eco Uc3m Es Docencia Matematicasii English Exercises I Problemas3 Pdf




Calc 501 1000 By James Bardo Issuu
Steps to use the derivative calculator Enter function you would like to differentiate and pay attention to the syntax checker tooltip which would inform you if the function is misspelled Enter differentiation variable if it is different from the default value Choose degree of differentiation Click 'Compute' button212 Partial Derivative as a Slope Example 26 Find the slope of the line that is parallel to the xzplane and tangent to the surface z x at the point x Py(1, 3, 2) Solution Given f x y x x y( , ) WANT (1,3) f x ( ) (1 0) 2 1 ( , ) ( )1 2 1 2 f x y x y x x y x x y x x y 2 Thus the required slope, 4 9 2 1 3 1 (1, 3) 1 3 fx 213 Partial Derivative as a Rate of Change A partial derivative is In this section we will the idea of partial derivatives We will give the formal definition of the partial derivative as well as the standard notations and how to compute them in practice (ie without the use of the definition) As you will see if you can do derivatives of functions of one variable you won't have much of an issue with partial derivatives




Partial Derivative Of F X Y Z With Respect To Z Mathematics Stack Exchange



What Is The Partial Differentiation Of X 2 A 2 U 2 Y 2 A 2 U 2 Z 2 A 2 U 2 1 With Respect To X Quora
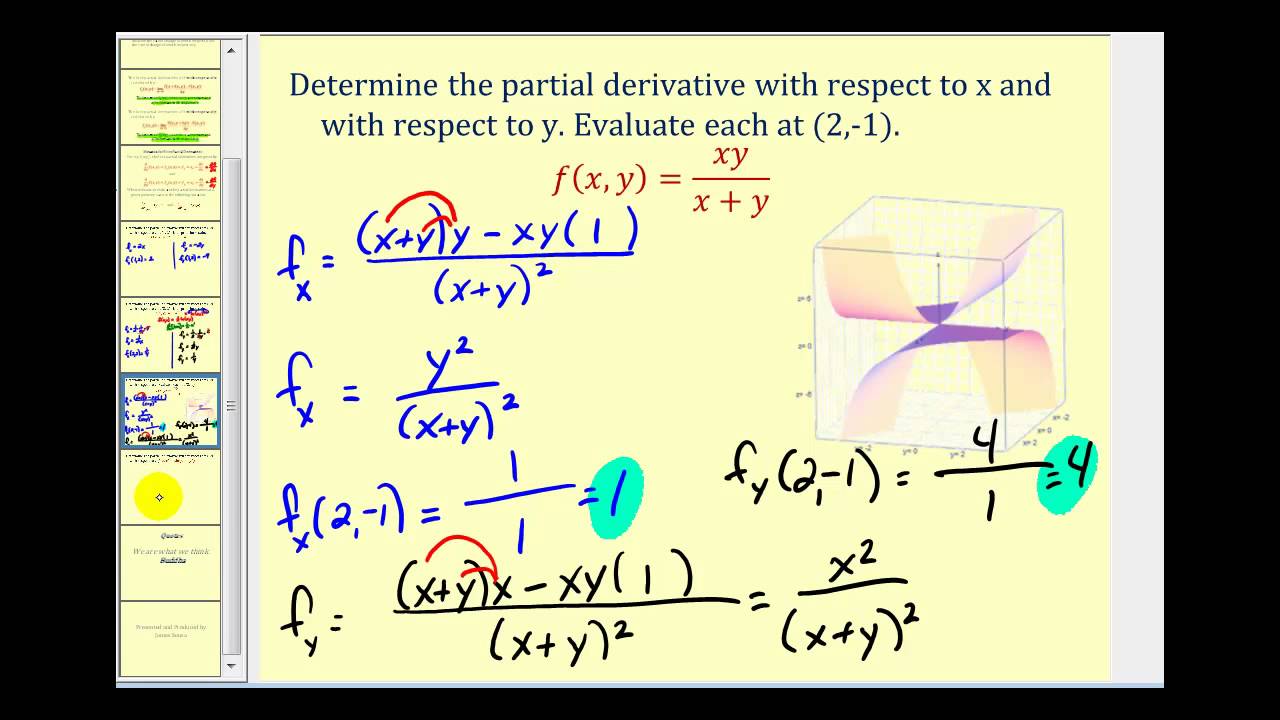
Find all first partial derivatives of the following function \(\displaystyle{f{{\left({x},{y}\right)}}}={y}{\cos{{\left({x}^{{{2}}}{y}^{{{2}}}\right)}}}\)Estimate the partial derivatives \(f_x(2,1)\) and \(f_y(2,1)\text{}\) Determine whether the secondorder partial derivative \(f_{xx}(2,1)\) is positive or negative, and explain your thinking Determine whether the secondorder partial derivative \(f_{yy}(2,1)\) is positive or negative, and explain your thinking Determine whether the secondorder partial derivative \(f_{xy}(2,1)\) is positive The partial derivative of f with respect to x is fx(x, y) = lim h → 0f(x h, y) − f(x, y) h The partial derivative of f with respect to y is fy(x, y) = lim h → 0f(x, y h) − f(x, y) h Note Alternate notations for fx(x, y) include ∂ ∂xf(x, y), ∂f ∂x,




Solucionario De Ecuaciones Diferenciales Y Problemas Con Valores En L



Solved Find All The First And Second Order Partial Derivatives Of F X Y X 2y 2 E Xy Sin X 2y Course Hero
Given below are some of the examples on Partial Derivatives Question 1 Determine the partial derivative of a function f x and f y if f(x, y) is given by f(x, y) = tan(xy) sin x Solution Given function is f(x, y) = tan(xy) sin x Derivative of a function with respect to x is given as followsThe origin is the level curve 0;Partial Derivatives Educators Section 1 Functions of Several Variables 0129 Problem 1 (x^{2}y^{2}1\right)$$ Regina H Numerade Educator 0351 Problem 30 In Exercises $1730,$ (a) find the function's domain, (b) find the function's range, ( c) describe the function's level curves, (d) find the boundary of the function's domain, (e) determine if the domain is an open region, a




Partial Derivative Calculator V2 Geogebra



Chapter Vi
And the cross derivative gives d^2z/dxdy = 1/(x^2 y^2) 2x^2/(x^2 y^2)^2;Engineering in your pocket Now study onthego Find useful content for your engineering study here Questions, answers, tags All in one app! #(del)/(dely)(x^2 y^2 z^2) = 0 2y 0# The same is true for the deivative with respect to #z# #(del)/(delz)(x^2 y^2 z^2) = 0 0 2z# This means that you have #(delw)/(dely) = color(green)(y/sqrt(x^2 y^2 z^2))# and #(delw)/(delx) = color(green)(z/sqrt(x^2 y^2 z^2))#




Multivariate Functions And Partial Derivatives Sage Research Methods




Functions Of Several Variables 13 Copyright C Cengage Learning All Rights Reserved Ppt Download
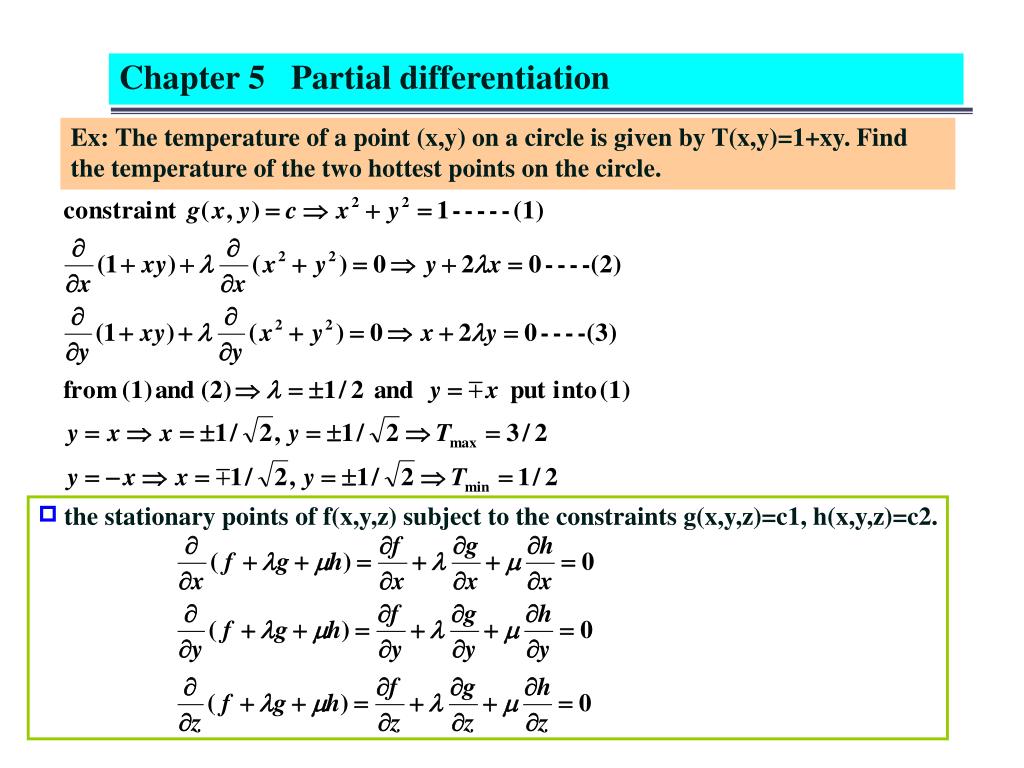
For the partial derivative with respect to h we hold r constant f' h = π r 2 (1)= π r 2 (π and r 2 are constants, and the derivative of h with respect to h is 1) It says "as only the height changes (by the tiniest amount), the volume changes by π r 2 " It is like we add the thinnest disk on top with a circle's area of π r 2C) on the left, two level curves are labeled;2 3) Solution We have z = (1 ¡ x2 ¡ y2)1=2 We want @z @y when 3




Answered Homework 3 Due Tuesday November 27th Bartleby




Lecture Pdf Partial Differential Equation Tension Physics
Partial Derivatives 1 Functions of two or more variables In many situations a quantity (variable) of interest depends on two or more other quantities (variables), eg h b Figure 1 bis the base length of the triangle, his the height of the triangle, His the height of the cylinder The area of the triangle and the base of the cylinder A= 1 2 bh The volume of the cylinder V = AH= 1 2 bhH TheU_x = (y/z)*x^((y/z)1) u_y = lnx/z?Question What are first and second order partial derivatives of Solution Given function let's substitute Part (1) It's First order partial derivatives are and



Http U Osu Edu Erchenko 1 Files 18 08 Homework 1 Solutions 2ig1w0w Pdf



Http Legacy Www Math Harvard Edu Knill Teaching Summer13 Handouts Week3 Pdf
Functions and Partial Derivatives 2A1 In the pictures below, not all of the level curves are labeled In (c) and (d), the picture is the same, but the labelings are different In more detail b) the origin is the level curve 0;Free partial derivative calculator partial differentiation solver stepbystep This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience By using this website, you agree to our Cookie Policy Learn more Accept Solutions Graphing Practice; To find d/dx(sqrt(x^2y^2)), as part of an implicit differentiation problem, use the chain rule d/dx(sqrtx) = 1/(2sqrtx), so d/dx(sqrtu) = 1/(2sqrtu) (du)/dx d/dx(sqrt(x^2y^2)) = 1/(2sqrt(x^2y^2)) * d/dx(x^2y^2) = 1/(2sqrt(x^2y^2))(2x2y dy/dx) =1/(2sqrt(x^2y^2))2x 1/(2sqrt(x^2y^2))2y dy/dx =x/sqrt(x^2y^2) y/sqrt(x^2y^2) dy/dx In order to solve for dy/dx



1 Partial Derivatives Of F X Y Xy Y Xy Are F Y 2xy Y



Http Www Eco Uc3m Es Docencia Matematicasii English Exercises I Problemas3 Sol Pdf
It all looks good ∂/ ∂x x/√ (x^2 y^2 z^2 = √ (x^2 y^2 z^2) x (1/2)2x/√ (x^2 y^2 z^2 ) / (x^2 y^2 z^2) then you multiply top and bottom of the fraction by √ (x^2 y^2 z^2) to get x^2 y^2 z^2 x^2 / (x^2 y^2 z^2)√ (x^2 y^2 z^2) I am new to partial derivatives and they seem pretty easy, but I am having trouble with this one $$\frac{\partial}{\partial x} \ln(x^2y^2)$$ now if this was just $\frac{d}{dx}\ln(x^2)$ we would get $\frac{2x}{x^2}$ So I feel we would get$$\frac{\partial}{\partial x} \ln(x^2y^2)=\frac{2x}{x^2y^2}$$Partial Fraction Decomposition of 1/(x^25x+6) Video Example of Sketching a Gradient Vector, and Level Curve Partial Derivative with respect to x of tan^1(x/y)




Get Answer 3 Find The First Partial Derivatives 1 X Y 2 32xy F Transtutors




First Partial Derivatives Calculus Iii Exam Docsity
Share the Solution Introduction In this this question and solution, we will find first and second order partial derivatives of z=f (x^2y^2)?I'm not really sure how to do these right =/ I would really appreciate any helpExample 1 Find the partial derivatives f x and f y if f(x , y) is given by f(x,y) = x^2 y 2 x y Solution to Example 1 Assume y is constant and differentiate with respect to x to obtain f_x = \frac{\partial f}{\partial x} = \frac{\partial}{\partial x}(x^2 y 2 x y ) \\\\ = \frac{\partial}{\partial x}(x^2 y ) \frac{\partial}{\partial x}(2 x) \frac{\partial}{\partial x}( y ) = 2 xy



Ppt 5 1 Definition Of The Partial Derivative Powerpoint Presentation Id
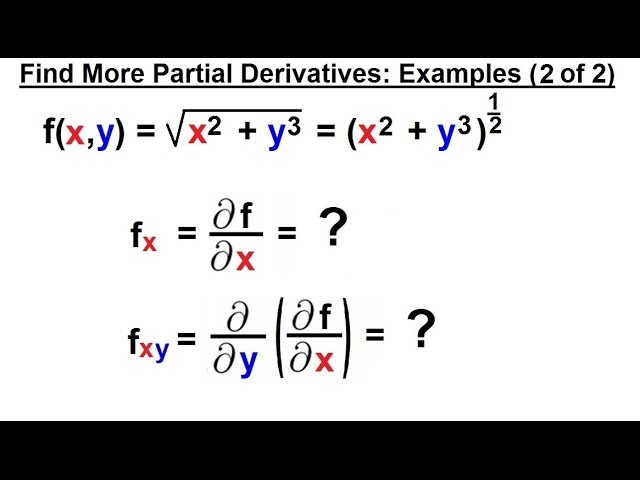



Calculus 3 Partial Derivative 14 Of 30 Find More Partial Derivatives Example 2 Of 2 Youtube
I believe these to be correct, however there may be sign errors in my workings out as I rattled through these quickly Any that aside, this is the general jist of how to do these derivatives, Hope this helps 0 reply sul Badges 14 Rep?1 First partial derivatives Thexxx partial derivative For a function of a single variable, y = f(x), changing the independent variable x leads to a corresponding change in the dependent variable y The rate of change of y with respect to x is given by the derivative, written df dx A similar situation occurs with functions of more than one variable For clarity we shall concentrate onPartial Derivatives and their Applications 265 Solution Given ( )2/2 2 2 22 m Vr r x y z== =mm (1) Here V xx denotes 2nd order partial derivative of V(x, y, z) with respect to x keeping y and z constant Thus ==∂∂ − ∂∂ (, z=,) ( ) ( ) 222 2 2 2 2221 2 mm x m V Vxy xyz xy z x xx 22 2 2 ()2 m mxxyz − = (2) and 222 ()1




Higher Derivatives Partial Differentiation




Find All The Second Order Partial Derivatives Of The Chegg Com
The limit definition of partial derivative at $(x,y)=(0,0)$ $$f_x(0,0)=\frac{\partial f}{\partial x}(0,0)=\lim_{h\to 0} \frac{f(0h,0)f(0,0)}{h}=\frac{\frac{(0h)\cdot 0\cdot ((0h)^^2)}{(0h)^^2}0}{h}=0;\\ f_y(0,0)=\frac{\partial f}{\partial y}(0,0)=\lim_{h\to 0} \frac{f(0,0h)f(0,0)}{h}=\frac{\frac{0\cdot(0h)\cdot (0^2(0h)^2)}{0^2(0h)^2}0}{h}=0$$ Note that $$f_x(x,y)=\frac{\partial f}{\partial x}=\frac{\partial f}{\partialY1 = f1 (x1,x2) y2 = f2 (x1,x2) ∗Each equation has two firstorder partial derivatives, so there are 2x2=4 firstorder partial derivatives — Jacobian matrix array of 2x2 firstorder partial derivatives, ordered as follows J= ∂y1 ∂x1 ∂y1 ∂x2 ∂y2 ∂x1 ∂y2 ∂x2 — Jacobian determinant determinant of Jacobian matrix Example 1 Suppose y1 = x1x2,and y2 = x1 x2Then the



2



Http Www Ucl Ac Uk Ucahmdl Lessonplans Lesson4 Pdf




Partial Differentiation If Z X Y X 2 Y 2 Show That әz әx әz әy 2 4 1 әz әx әz әy Youtube




Answered 7 Find The Second Partial Derivatives Bartleby



Users Math Msu Edu Users Gnagy Teaching 06 Summer S1 Mathc W5 C Pdf




Find The First And The Second Order Partial Chegg Com



Http Www Cns Gatech Edu Predrag Courses Phys 6124 11 Stgochap6 Pdf
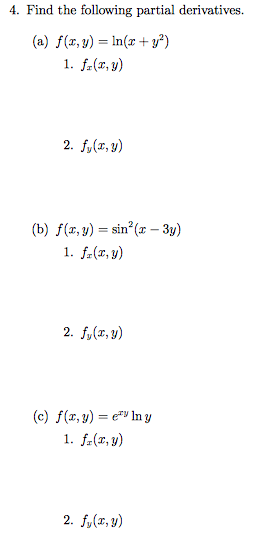



4 Find The Following Partial Derivatives A Chegg Com




Derivative Calculator Wolfram Alpha
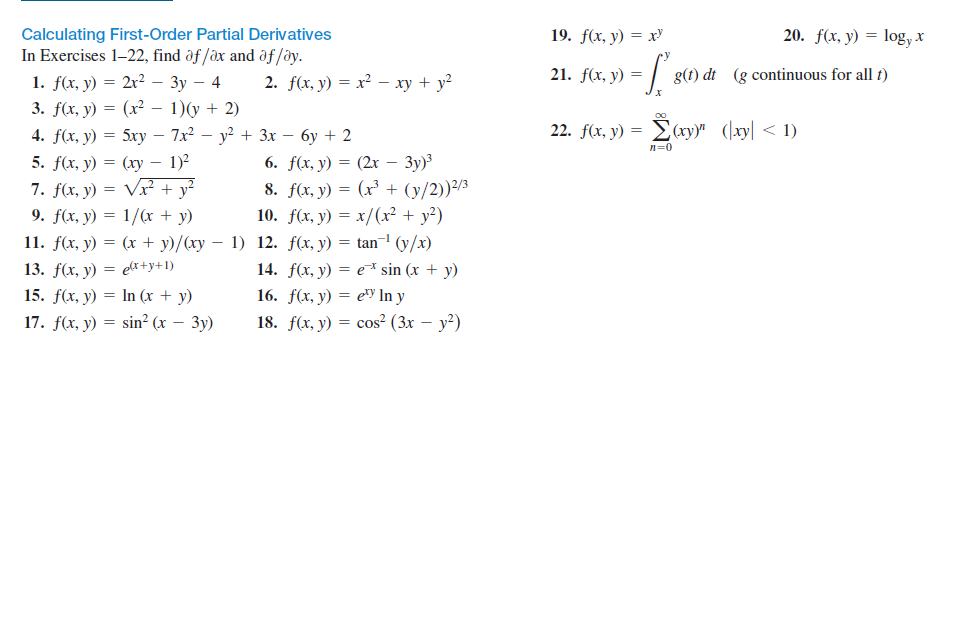



Answered Calculating First Order Partial Bartleby




Doc Chapter Four Derivatives Of Multivariate Functions Partial Differentiation Habtamu Destaw Academia Edu
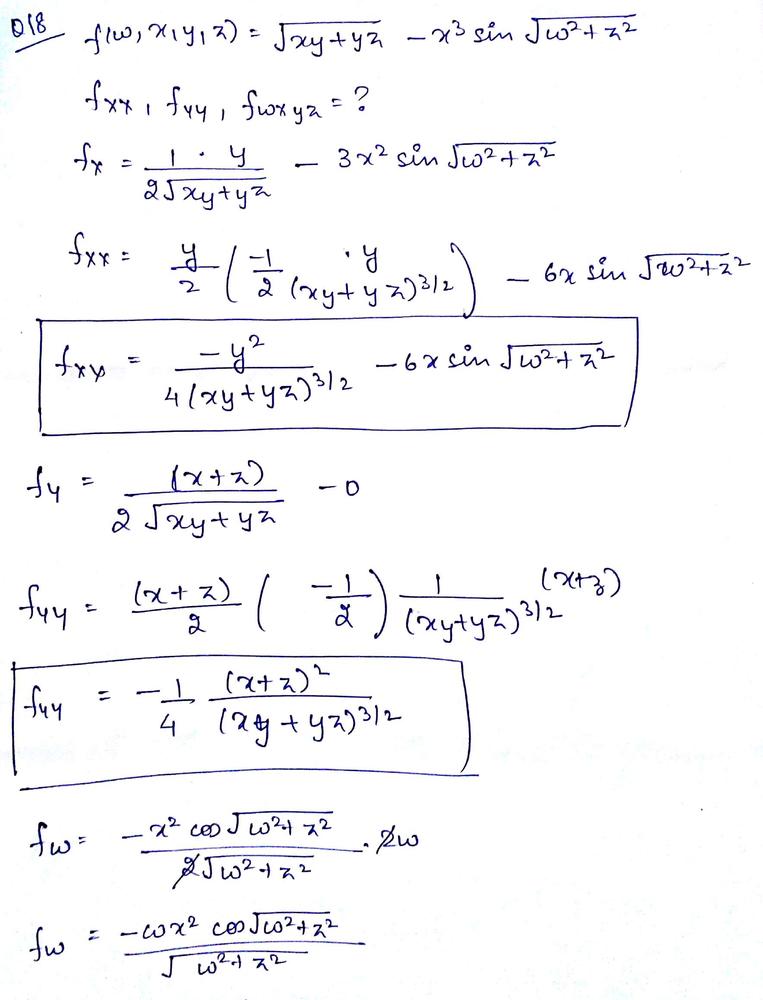



Find The Indicated Partial Derivatives Math F W X Y Z Sqrt X Y Y Z X 3 Sin Sqrt W 2 Z 2 F X X F Y Y F W X Y Z Math Homework Help And Answers Slader



Users Math Msu Edu Users Gnagy Teaching 11 Fall Mth234 Mth234 009 E2 F10 Pdf




15 Partial Derivatives Partial Derivatives 15 3 Partial



Www Ualberta Ca Rjia Math214 Hwks Sol8 Pdf



Partial Derivatives



1



Find The Partial Derivatives Of The Following Functions At The Indicated Points I F X Y 3x 2 2xy Y 2 5x 2 2 5 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Partial Derivatives And Differentiability Sect 14 3 Flip Ebook Pages 1 Anyflip Anyflip



Http Mathweb Math Ncu Edu Tw Calc 98s Assist Hw 98s Hw3 Pdf




Partial Derivatives Practice Studocu




Partial Derivatives Worksheet Need Help With Answers Maths



Partial Derivatives Calculus Volume 3



Http Www Utm Utoronto Ca Asc Sites Files Asc Public Shared Pdf Tip Sheets Math Rgasc Cmath Partial derivatives 1117 Pdf



Ex 9 4 11 Find Particular Solution X3 X2 X 1 Dy Dx



3




Find All The First Order Partial Derivatives For The Chegg Com



Solved Find The First Partial Derivatives Of F 5 2x 28 2 28 At The Point 7 4 2 Or 4 2 On Dy 4 2 Course Hero



Ex 9 4 11 Find Particular Solution X3 X2 X 1 Dy Dx




Partial F X Y X F X X2 Y2 And Then We Evaluate The Derivative As If Y Is A Constant Pdf Free Download




Copyright C Cengage Learning All Rights Reserved Partial Derivatives Ppt Download



Http Mathsci Kaist Ac Kr Dykwak Courses Calfall Veccal Main 14 Pdf



Http Www Tcd Ie Economics Staff Ppwalsh Twovarsol Pdf




Partial Derivative Examples Math Insight



What Is The Partial Derivative Of U Y X W R T To X And Y Quora




Find The Indicated Second Order Partial Derivatives Chegg Com




Homework 14 5




Let F R2 R Be Given By Z Y 0 0 R Y 2y And F 0 0 Homeworklib



Find The Partial Derivative Of F X Y E X2 Y2 With Chegg Com




Eli5 Partial Derivatives Explainlikeimfive




Copyright C Cengage Learning All Rights Reserved 14 Partial Derivatives Ppt Download




Derivatives And Partial Derivatives Derivative Subtraction
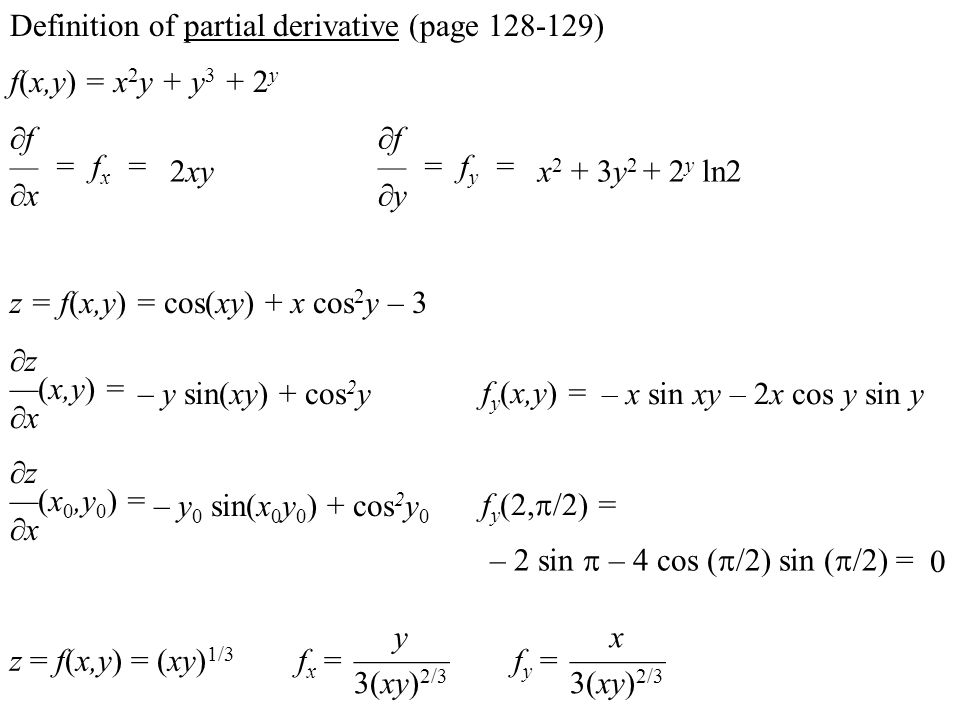



F X Y X 2 Y Y Y F F X X 2xyx 2 3y Y Ln2 Z F X Y Cos Xy X Cos 2




Review Of Partial Derivatives Bruce E Shapiro




14 Partial Derivatives Partial Derivatives In Example 6



Http Www2 Gcc Edu Dept Math Faculty Bancrofted Teaching Handouts Partial Derivatives Pdf



Partial Derivative Of F X Y Xy X 2 Y 2 With Quotient Rule Youtube




Partial Derivatives Calculus 3




Limits And Continuity Pdf Free Download



What Is The Differentiation Of 1 X 2 Quora




Answered 2 Evaluate The Limit Using The Bartleby




Worksheet Partial Differentiation Applications Differential Topology Subtraction




Consider The Function F X Y Ln X 2 Y 2 3 Compute The Partial Derivatives Of The First And Second Order Mathematics Stack Exchange
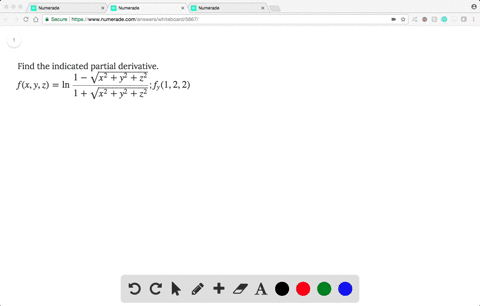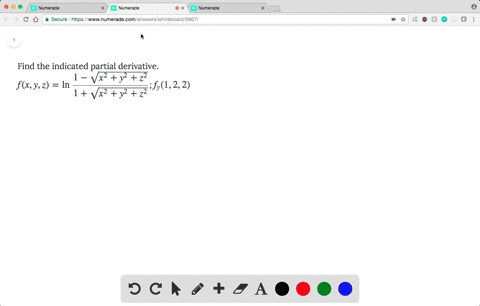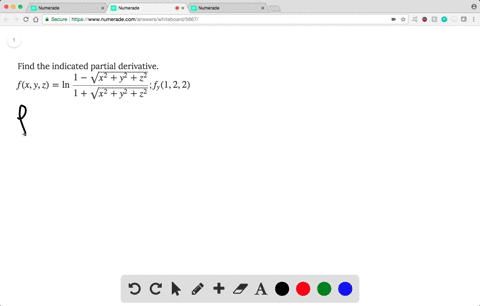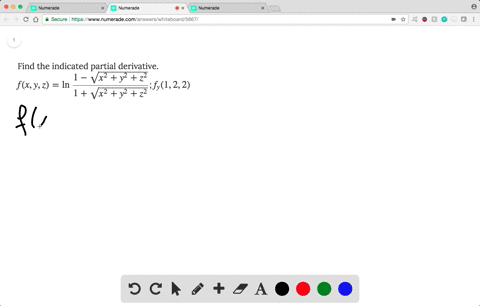



Solved Find The Indicated Partial Derivative F X




Assgn1a Derivative Continuous Function



Http Math Depaul Edu Kliechty Math255 Homework Hw06 Solu Pdf



Http Www Math Ntu Edu Tw Cheng Teaching Calculus Ch15 Pdf



1



Rules Of Calculus Multivariate



Calculus 3 Partial Derivative 7 Of 30 Find The Partial Derivative Example 3 Youtube



Www Math Cuhk Edu Hk Course Builder 1718 Math10e Tutorial6 Pdf




Find All The First Order Partial Derivatives For The Chegg Com



Partial Differential Equation Notes



Http Maths Dur Ac Uk Users Daniel Evans Mes Messolutionsupdated Pdf



Www Ucl Ac Uk Ucahjva Multi4 Pdf




Calculus Pages 501 550 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5



2




Partial Derivative Math Help Forum



Q Tbn And9gcrrinrx Cj Exg3nxzq0njw Zkgdtymbulzjk0knpmztrmnoi4q Usqp Cau




Confirm That The Mixed Second Order Partial Derivatives Of F Are The Same F X Y Sqrt X 2 Y 2 Homework Help And Answers Slader
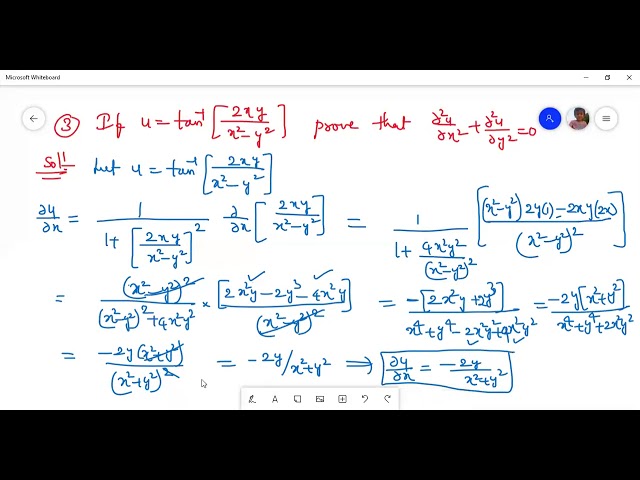



Problems On Partial Differentiation U Log X 2 Y 2 Z 2 U Tan 1 2xy X 2 Y 2 Z F X Ay Q X Ay Youtube



Http Www Mast Queensu Ca Math121 Assignmentsolutions Sol S14 07 Pdf


